Difference between revisions of "Solar Heat Energy Demonstrator"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Shed2.png|thumb| | [[File:Shed2.png|thumb|428x428px|Google Earth]][[File:Shed1.png|thumb|427x427px|Google Earth]] | ||
== To Do: == | == To Do: == | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
* Detailed design of pipework and equipment | * Detailed design of pipework and equipment | ||
== | == Aims == | ||
The aim of the project is two-fold. Primarily it is to provide better heating for the building using low carbon heat, bringing the building up to a suitable level of heating to be passed on to the next occupants. However, the project is also been run as a laboratory test to work out the best practices and installation choices, to maximise in-use efficiency of CO2 heat pump technology, and work out it's place in the renewables landscape for the future. | |||
== Requirements == | |||
Following initial site meetings the following requirements have been set: | |||
* Installation of CO2 air source heat pump(s) | |||
* Low use domestic hot water | |||
* Central heating to 10 office spaces | |||
* Office spaces to be fitted with a selection of heat emitter types | |||
* System to be flexible enough to allow different heating strategies to be tested | |||
* System must be of a standard to be handed over to the next building occupants | |||
* System must allow for the optional use of fan convectors as final stage to heat the main area and lower return temperatures | |||
* System to be provide real-time operational data and allow details adjustment of settings and controls logic | |||
== Heat Pump Selection == | == Heat Pump Selection == | ||
[[File:Qavh.png|thumb|Mitsubishi Electric QAVG 40kW CO2 Air Source Heat Pump]] | [[File:Qavh.png|thumb|Mitsubishi Electric QAVG 40kW CO2 Air Source Heat Pump]] | ||
Revision as of 01:09, 11 June 2022
To Do:
- Review designs and calculate loads
- Produce schematic of proposed design
- Detailed design of pipework and equipment
Aims
The aim of the project is two-fold. Primarily it is to provide better heating for the building using low carbon heat, bringing the building up to a suitable level of heating to be passed on to the next occupants. However, the project is also been run as a laboratory test to work out the best practices and installation choices, to maximise in-use efficiency of CO2 heat pump technology, and work out it's place in the renewables landscape for the future.
Requirements
Following initial site meetings the following requirements have been set:
- Installation of CO2 air source heat pump(s)
- Low use domestic hot water
- Central heating to 10 office spaces
- Office spaces to be fitted with a selection of heat emitter types
- System to be flexible enough to allow different heating strategies to be tested
- System must be of a standard to be handed over to the next building occupants
- System must allow for the optional use of fan convectors as final stage to heat the main area and lower return temperatures
- System to be provide real-time operational data and allow details adjustment of settings and controls logic
Heat Pump Selection
Selection
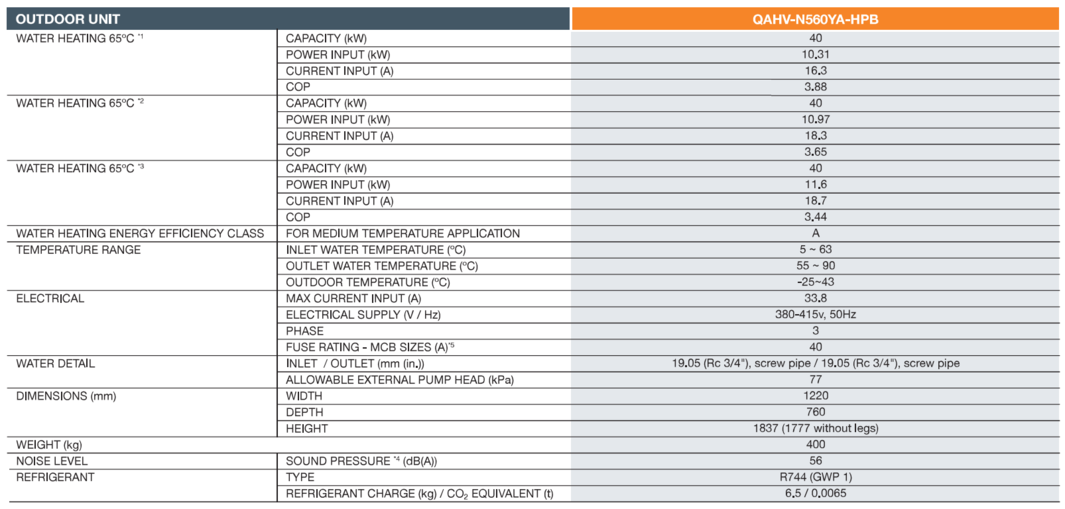
The selected heat pump is a Mitsubishi Electric QAVG 40kW CO2 Air Source Heat Pump.
Specifically designed for commercial sanitary hot water application, where gas boilers, combined heat and power systems (CHP) or electric water heating have been traditionally utilised, the QAHV provides a low carbon solution for hospitals, hotels, leisure centres and student accommodation. Utilising the natural and stable refrigerant CO2 (R744), the environmentally clean solution enables compliance to strict local planning laws and boosts BREEAM points. Compounded by the increasing decarbonisation of the electrical grid and the UK’s commitment to Net Zero 2050, the QAHV provides a high efficiency, low carbon hot water delivery solution with leaving water temperature up to 90°C.
Documentation
![]() QAHV_6PP_AW_v2
QAHV_6PP_AW_v2
![]() QAHV-N560YA-HPB_Service_Manual
QAHV-N560YA-HPB_Service_Manual
![]() QAHV-N560YA-HPB_Install_Manual
QAHV-N560YA-HPB_Install_Manual
![]() QAHV-N560YA-HPB-PI-SHEET
QAHV-N560YA-HPB-PI-SHEET
Technical Specifications
Sizing
Bivalent Systems for Heat Networks
The following designs show the impact of a single 40kW heat pump on various numbers of properties. This is unrelated to the SHED, however is shown in order to give the reader a feel for the impact of even a single heat pump on real-world loads.
Each property is 2 bedroom 3 person, and 4kW heating load.
Topping up boilers are included to achieve peak loads.
| Properties | % Heat Pump | Design Link |
|---|---|---|
| 20 x 2B3P | 99.9% | https://hw7.ddns.net/ui/hndesign?loadCID=QmNg4trTmoxkD35qj4eBWd1exKwKfbVpP3jRNgEQwZn4qB |
| 30 x 2B3P | 94.6% | https://hw7.ddns.net/ui/hndesign?loadCID=QmXz5H1sdV5F1juQrQc71PLjdWCPWkHhqHkitGbC8o8B9z |
| 40 x 2B3P | 83.6% | https://hw7.ddns.net/ui/hndesign?loadCID=QmPgBB6jSXehwP2ZYp7LcZNQeEyXggQM4FPgcgdQWQgZVc |
This graph shows how the vast majority of load (for 2021) is driven by heat pumps (blue & orange), with boilers (green) used to top up.