Difference between revisions of "Putney Plaza"
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
<pre class="wikidiagrams"> | <pre class="wikidiagrams"> | ||
heatweb_zcccaef4ahl.json Boiler Controller | heatweb_zcccaef4ahl.json Boiler Controller | ||
heatweb_putney_heat_meter_1.json Heat Meter | heatweb_putney_heat_meter_1.json Heat Meter | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 23:52, 3 November 2022
To Do
- Investigate current state of heat pumps and CHP
- Install heat meters and controls
- Confirm current operation
- Recommission
- Remote dashboards
Existing Documentation
2022 Plan
- Get internet to panel
Completed 26/09/22 - Confirm readings from 4 new boiler sensors
Completed 26/09/22 - Obtain remote access to new Internet Router
- Install VPN
- Add sensors to CHP (flow / return)
- Install new MQTT services into cloud server using Docker (data send directly to server)
Completed 26/09/22 - Install Grafana and update cloud server dashboard and wiki with new data
- Regain control over boiler valves from new panel.
- Update controller in tank room for buffer/boiler control, and replace buffer sensors. This will provide renewed monitoring and control over the boiler circuits.
- Update sensors in each buffer tank Rewire boiler demand switch
- Fit a control panel on one of the roof tops, a well as a board inside the existing control panel. The new panel will be used to collect data and establish permanent requirements that will then be implemented via existing panel. We need to better understand what the existing panels wire to, then rewire sensors and outputs to the new controller to reinstate operation.
- Once one heat pump is working and visible, the others can be addressed.
- Reinstate heat meter when boilers ready for a workout
- Fully commission boilers and valves
- Update boiler pump to a Magna3D for variable speed control.
BMS Controls
- No visibility on existing Trend controls.
- No way to check or alter controls logic.
- No separation in trunking between high and low voltage cables.
Issue with Internet Connectivity
The site has been plagued with internet connectivity problems resulting from changes in internet provider. This has resulted in long periods without access to controls or visibility.
Key lessons learned from the experiences include:
- You only require standard simple internet, with no fancy management. A standard domestic connection is perfect.
- Routers should have the standard functions including:
- Remote access via either http or https
- The ability to setup port forwarding
- A fixed IP address is preferred. Dynamic DNS services can be used instead, however there may be occasional loss of connections as IP addresses update when they change.
- With engineer rates in the £100s per day, changing an internet setup to save a few pounds is a false economy that requires an engineer to attend site and reinstate port forwarding rules etc.
- Routers should be safe from tampering and accidental damage. A locked BMS cabinet is the preferred position.
- Where internet is not already available as per preceding points, a GSM modem should be included in the initial fit. It is common for phone lines and internet providers to take weeks if not months to get everything in place. Connectivity should be available from the first day on site.
Air Source Heat Pumps
An initial survey of the roof top heat pump systems has highlighted some significant problems.
- No way to understand current operation, without any feed into a monitoring (SCADA) system.
- No alarming
- No performance monitoring
Next Steps
- Obtain all relevant manufacturers instructions on heat pumps and fitted controls
- Upgrade controls with open control system and remote monitoring so that the heat pumps can be setup and controlled as required
- Recommission heat pumps using new system
- Monitor performance and setup alarm routes
Boilers
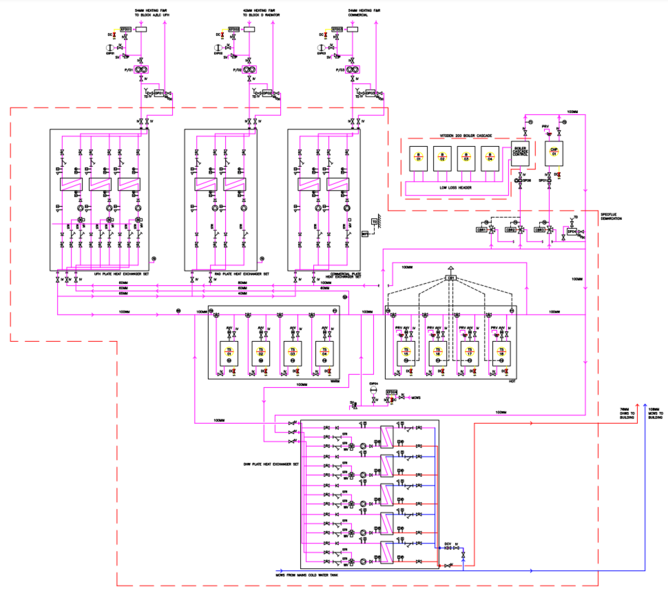
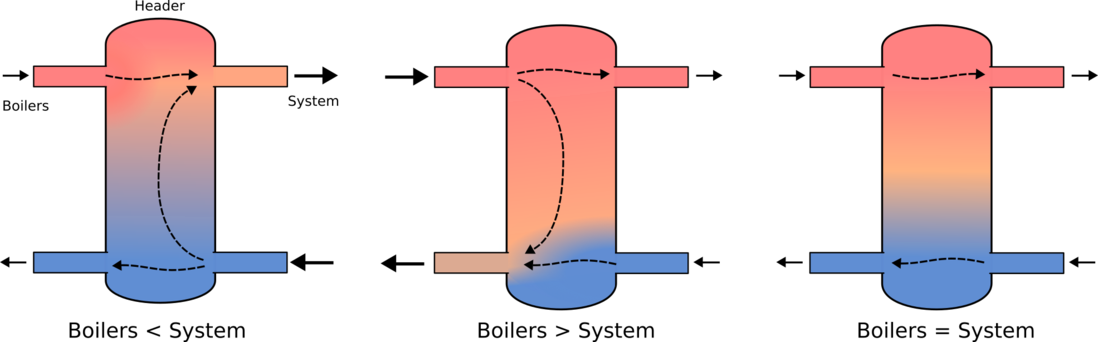
Hydraulic Arrangement
Correct Function
- Boilers should be sequenced from buffer stores. As each of the four series buffers deplete in temperature, an additional boiler should fire up.
- Lead boilers should be rotated.
- The flow rate through the boilers is controlled (via pump speed) by the boiler (or is manually set) and cannot be externally controlled. The flow rate will allow for a maximum temperature drop across the boiler, of 20C.
- Loading valves are fitted to the back end of the boilers. These are modulated to maintain a minimum temperature into the header from the system, preventing water colder than 55C from entering the boilers, however the use of a header makes the valves potentially redundant. [They are currently uncontrolled]
- The shunt pump between the header and the buffer storage must be controlled to remove the heat from all firing boilers, maintaining flow temperatures across the header, with a varying number of boilers firing and fluctuations in return temperature. As such it needs to modulate depending on the temperatures across the header.
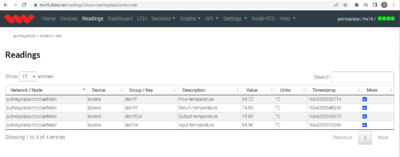
Measuring Boiler Outputs
A Micronics Clamp-On Heat Meter has been temporarily installed onto boilers in order to confirm the peak outputs of each boiler.
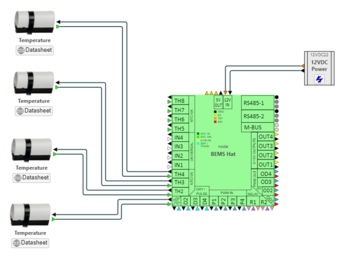
Wiring New NTC Sensors
heatweb_zcccaef4ahl.json Boiler Controller heatweb_putney_heat_meter_1.json Heat Meter
https://hwwiki.ddns.net/ui/wiring/wiring22/QmUHopoYv7NE5QUYppfTxaaLoRni4QjjNkAPpkXadFhmvf
Initial Findings
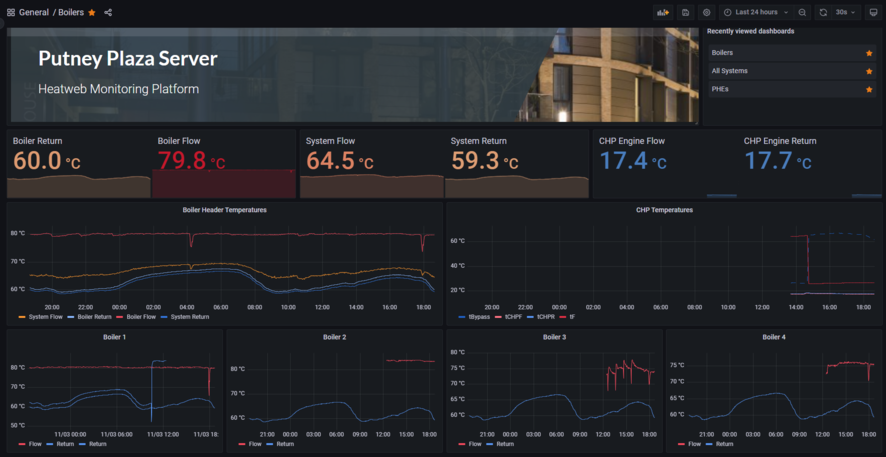
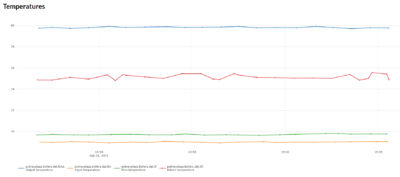
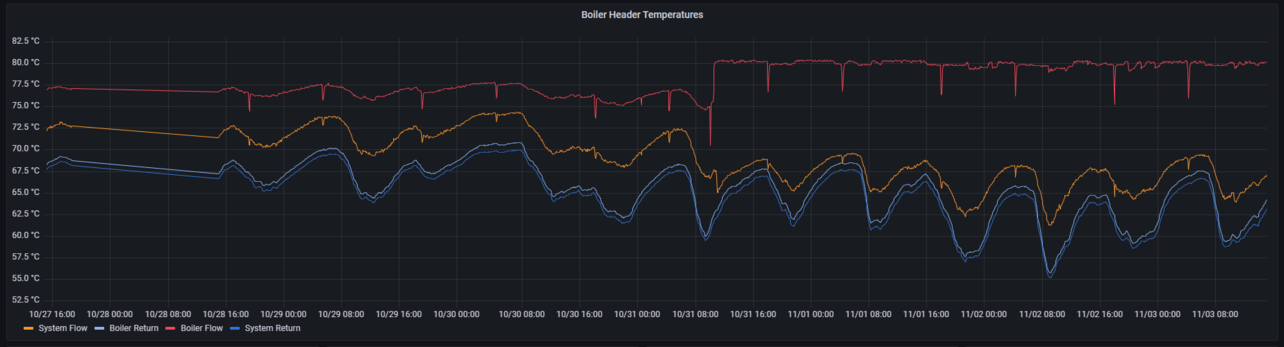
As part of the upgrades we are moving the client interface into Grafana. The image below shows the initial dashboard created to show the boiler temperatures.
Viewing the data highlights a few things...
- We have data resolution higher than needed, with every reading coming through, almost every second. This uses up more SIM data than needed, and results in graphs taking longer to load, with a vast number of data points to load if looking at a few days data. To correct this we placed a "Report By Exception" rule, whereby data is only sent every minute, or if it changes by more than 0.5C since the last send. This way, when there is little movement in temperatures we get a data point every minute, but when temperatures change rapidly, we get higher resolution (down to every second) so we don't miss anything interesting. The difference can be seen in the graph, looking at the orange System Flow reading, where the change results in less data points.
- The System Flow temperature is nearer the return than the blow from the boilers. This means that the system flow rates are roughly double the boiler flow rates. This causes unnecessary mixing and we lose the higher boiler temperatures. It is clear that the method of controlling pump speed needs examining, potentially introducing pump speed control and tying it in with boiler sequencing.
- The system return temperature is roughly 65C, which is too high.
https://hw16.ddns.net/dashboard/snapshot/fAqR4khHc24jSY6TKq1ZqMbEeRvrVFYg?orgId=1&refresh=30s
Header Control
The current fixed speed shunt pump between the header and the storage tanks is not compatible with boiler sequencing, where the output varies with the number of boilers firing and the shunt pump needs to vary to match output.
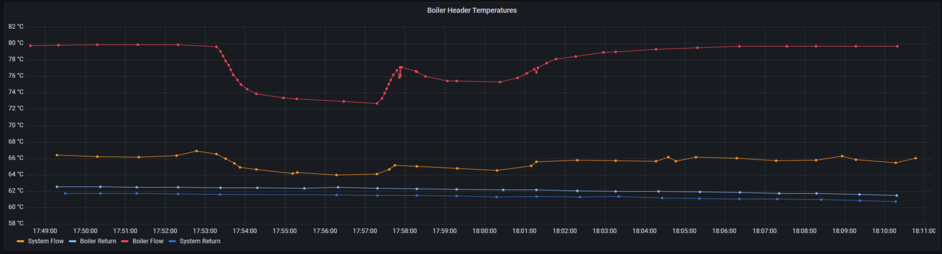
The following graphs shows 1 week of operation. On 31st at 10:30 the boiler outputs can be seen to change in profile to a steady 80C flow temperature. This is as a result of ongoing boiler works, and is believed to result from a change in pump speed, reducing the flow rate through the boiler so it is able to achieve target temperature of 80C.
https://hw16.ddns.net/dashboard/snapshot/SSo8vPROq9xZmOLr7cr0t8pSObu5Jiyc
What this clearly shows is that the boilers are generating 80C heat, but the system rarely sees 70C, because the flow rates are much higher on the system side. This indicates that the system side pump needs better control, so that flow rates are better matched to boilers, and the boiler flow temperatures reach thermal stores. As the pump is slowed down, the system flow temperature will increase. Once it has dropped to match the boilers, the 80C to the system (orange) will be very close to the boiler supply (red).
If pump flow rates are dropped too far, then not all the heat generated will be removed and boilers will modulate down and start cycling significantly. This is why a fixed speed approach can never work.
To implement a simple control logic we would vary system side flow rates to achieve an equal temperature difference between the hot pipes as the cold pipes.
E.g. Boiler output is 80C, System flow is 77C (a 3C difference), so if System return is 60C, we control pump to achieve 63C on the return to the boilers (speed up to reduce return temp diff).
This maintains matched flow rates on the system side, and ensures boilers remain at full output until stores are satisfied. With the current fixed settings this has never been possible. At startup, when boilers may be sluggish to heat up, the system pump will be at a minimum speed (or off), only speeding up as boiler temperatures climb above 75C. This will prevent cold plugs making their way to heat exchangers.
Zooming in on one of the points of cycling (below), one can see the boiler turning off [17:53:20], followed by the pump off [17:54:00], followed by restart [17:57:15].
The entire cycle lasts approximately 10 minutes, repeating roughly every 10 hours when return temperatures are at their highest.
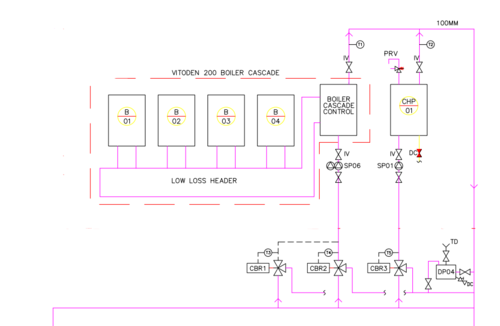
CHP
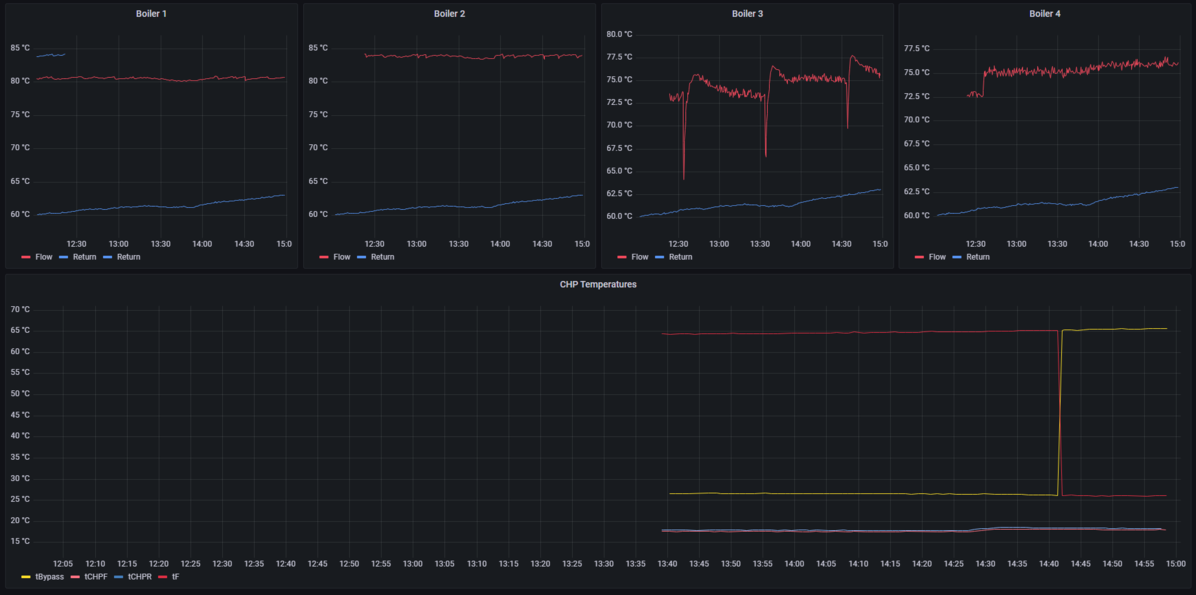
Temperature sensors have been added to individual boilers as well as the CHP, so we have clear indications on all plantroom heat sources.
- tBypass is the temperature on the section of boiler return the CHP is fitted across. This is the temperature of water fed to the CHP.
- tF is the temperature out of the CHP on the system, feeding into the boiler return.
- tCHPF is the CHP engine flow (coming directly out of the CHP before heat exchanger)
- tCHPR is the CHP engine return
Note that the red and yellow (flow and return) were labelled incorrectly, hence the swap in values when corrected.
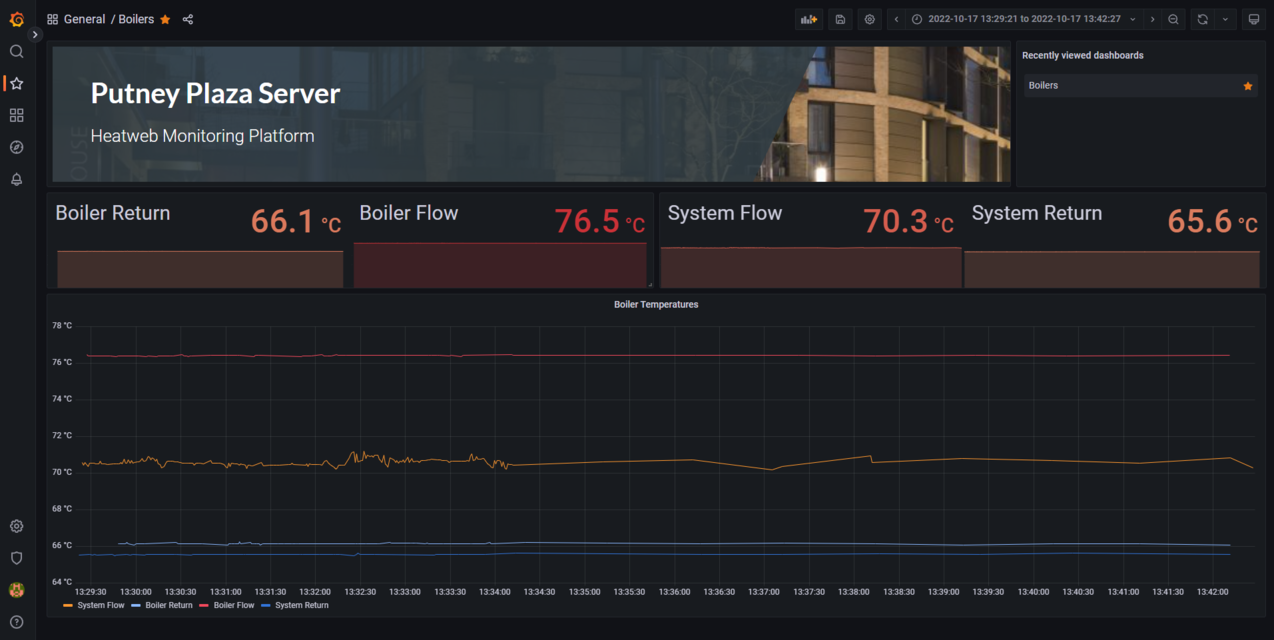
Client Dashboards
The latest Grafana user interface can be found at... https://hw16.ddns.net/
Login using putney-plaza for both username and password. (Note this may change without notice, but for now is open)