Difference between revisions of "Buffer Store Control"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* Heat sources are assigned an order, representing the preferred order in which they fire, with 1 being the lead. | * Heat sources are assigned an order, representing the preferred order in which they fire, with 1 being the lead. | ||
* Uncontrolled heat sources, such as solar thermal, has an order of 0. Heat will be taken if available and | * Uncontrolled heat sources, such as solar thermal, has an order of 0. Heat will be taken if available and safety controls allow. | ||
* Heat sources with the same order will be run in duty/standby and rotated, pulling in the next in order as required. | * Heat sources with the same order will be run in duty/standby and rotated, pulling in the next in order as required. | ||
* Heat sources are fired up according to store depletion, both on volume remaining and rate of depletion. | * Heat sources are fired up according to store depletion, both on volume remaining and rate of depletion. | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 24 May 2022
Functionality
- Heat sources are assigned an order, representing the preferred order in which they fire, with 1 being the lead.
- Uncontrolled heat sources, such as solar thermal, has an order of 0. Heat will be taken if available and safety controls allow.
- Heat sources with the same order will be run in duty/standby and rotated, pulling in the next in order as required.
- Heat sources are fired up according to store depletion, both on volume remaining and rate of depletion.
- Heat sources may be exercised after a period of inactivity, regardless of order.
- Modulation will be applied to heat sources where possible to match loads and minimise cycling.
- Low load buffering mode to minimise cycling.
- Timing functions can be applied.
- Includes functions for override of non-critical loads, such as central heating, when store close to empty.
- Includes functions for activation of heat dump circuits for solar thermal and biomass.
- Includes functions for boiler loading valve and pump control (with DP switch or sensor).
- Includes functions for network tempering valve control.
- Includes functions for M-Bus/Modbus heat meter reading.
- Includes alarm functions for low/high temperature, low/high pressure, low storage, failure of heat sources.
- Makes possible the implementation of storage management and sequencing based on volatile fuel prices using predicted loads
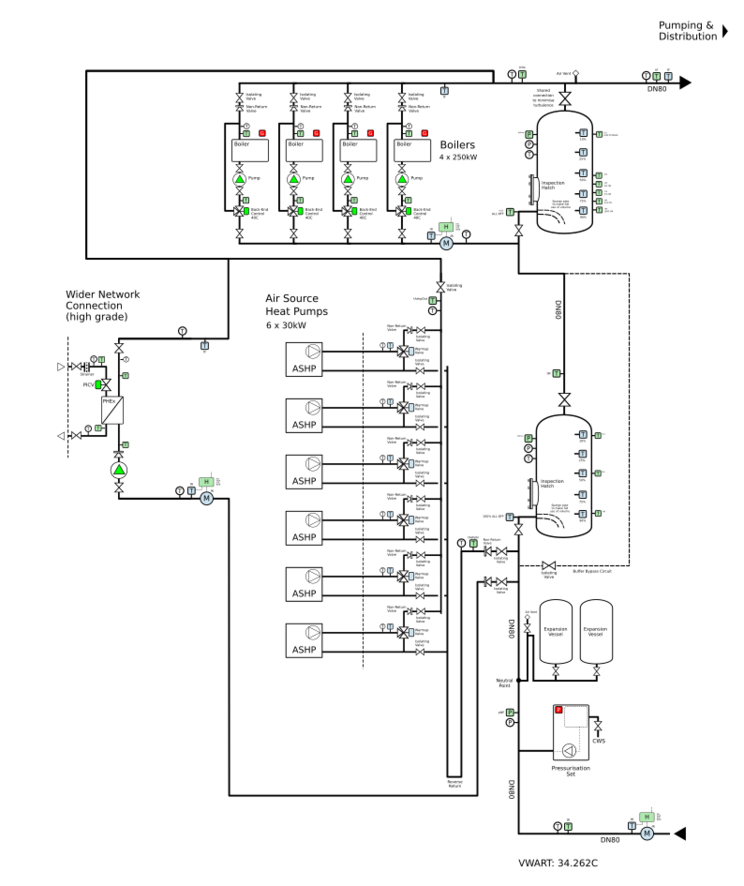
Schematics
The following schematic was generated using our open-source Heat Network Designer software.