Open Control Architecture
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
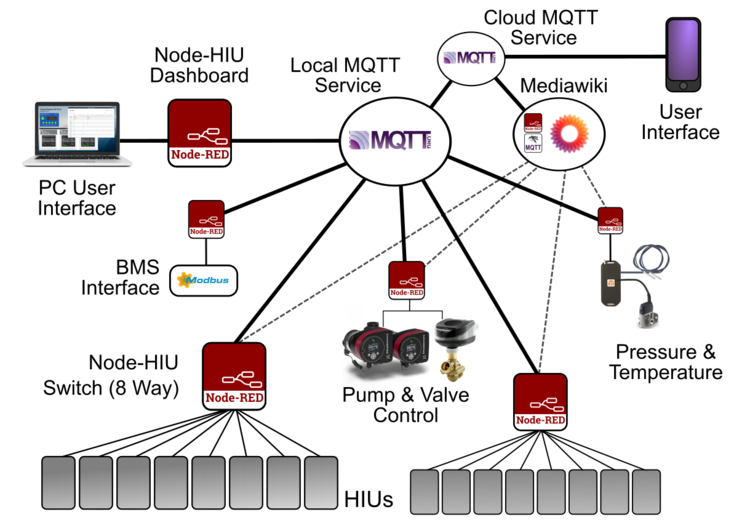
Controls software is written in Node-RED.
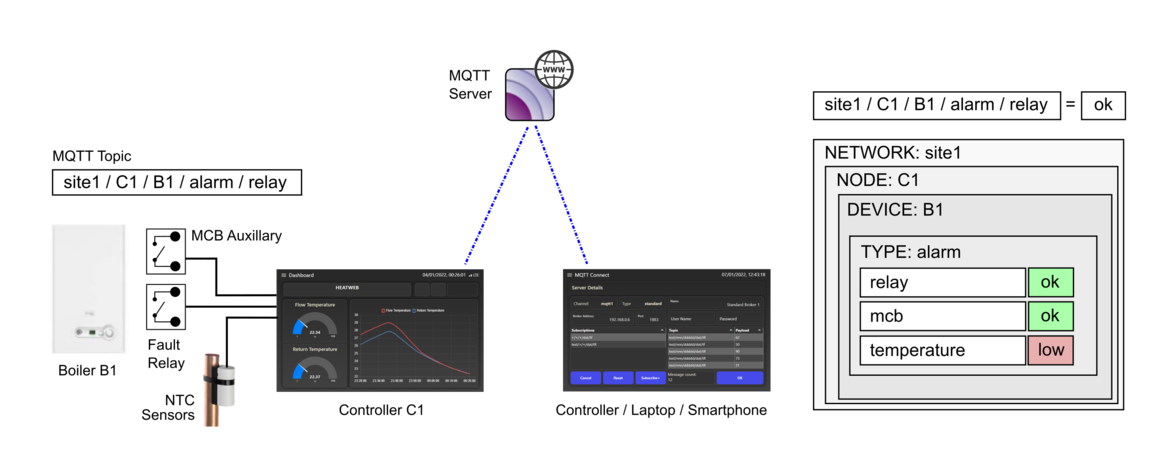
Communications between systems is performed using MQTT using a standardised 5 level topic structure. network / node / device / group / key.
Systems run a local MQTT broker to distribute data both internally and to enable external subscriptions.
A Node-RED system (controller or server) is called a node.
The node identifier is stored under global.node
The external network identifier, used for all data published to external MQTT brokers, is stored under global.networkId
Data from within a node or from connected devices is assigned a local network identifier of "local" (stored under global.localNetworkId) so that the node's external network identifier can be changed without affecting internal software. Separate internal and external identifiers also allows for separate message rates, where local traffic can be high speed, while external traffic can be throttled to save bandwidth.
The topic group is used to define the type of data. Values include:
- dat (operational data)
- stat (statistics and status)
- settings
- cmd (a command)
- set (change a setting)
- system (software and networking)
Attributes for data may be loaded from a central index (GitHub hosted), providing additional information such as units and descriptions. This is to avoid the need to locally describe data, and to assist in compatibility.
Within Node-RED, data and attributes are stored within the global.readings object.
The current data can be viewed in the data explorer.
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Historic data is saved into the global.readingsHistory object, in the same structure as global.readings, but containing an array of timestamped values.
Persistent settings for a node (or application) are held on disk and in the global.settings object. This is for local operational settings.
Settings have a type, may have maximum and minimum values, units and a title. Certain types require additional fields such as select from a list settings.
The snapshot below shows a variety of setting types including numeric/text values, html, or JSON objects and arrays.
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Persistent settings for local devices are held on disk and in the global.deviceSettings object, and are specific to a device (or node).
Data within the readings object is nested according to the topic (excluding the node as more than one node may publish data on a device).
e.g. a message with a topic myNetwork/node123/myDevice/dat/outputTemperature would be stored in (global).readings.myNetwork.myDevice.dat.outputTemperature.value
Internally, message topics can be truncated and the network and node will be filled in. The data group will be assumed to be "dat" if not supplied, representing operational data.
e.g. a message with a topic setpoint would be stored in (global).readings.local.myNode.dat.setpoint.value
The following code could be used to read data and its attributes for output.
var localNetworkId = global.get("localNetworkId");
var node = global.get("node");
var reading = global.get("readings." + localNetworkId + "." + node + ".dat.outputTemperature");
var output = "The value of " + reading.title + " is " + reading.value + reading.units;
// "The value of Output Temperature is 35°C